Main menu
You are here
Build a house - Earth Works ( Excavation,Filling and compacting - grading- Termite Control )
- Excavation,Filling and compacting
- Surveying works / grading work / Fix site corners
- Termite Control
Excavation
When the construction of a road or building is undertaken, the existing structures have to be demolished. Demolition is required for structures which are no longer wanted or are declared unsafe for further utilization. After demolition, excavation is carried out. In this process, the ground is excavated according to center-line drawing and the layout plan. Then benchmarks are set and survey is carried out. After the survey is carried out, the site is excavated to approve depth which is followed by dressing process. The dewatering wells and interconnecting trenches are constructed for use of water during construction. Then the boundaries are marked and protection bunds are constructed.
Excavation consists of the removal and disposal of materials encountered when establishing the required limits and grade elevations.
Excavate to elevations and dimensions indicated on the drawings or required for the work and approved by the Engineer.
Except where noted otherwise on the drawings, excavate and remove below grade portions of previous foundations, abandoned utilities, etc.
Remove from the site all debris and other excavated material not suitable for use as fill, to a dump area approved by competent authorities.
Rock or boulders encountered in the excavation shall be removed within required excavation limits and to such additional depth and extent as directed and authorized by the Engineer.
When excavation has reached the required sub grade elevation, notify the Engineer who will make an inspection of conditions to observe the strength and bearing capacity of the soils.
If disturbed and otherwise unsuitable bearing materials are encountered at the required sub grade elevations, carry excavations deeper and replace the excavated material with Lean Concrete Fill or Compacted Structural Granular Fill as directed by the Engineer.
Removal of disturbed material and its replacement as directed shall be at the Contractor's own expense.
In excavation for foundations, take care not to disturb the bottom of the excavation. Excavate by hand or smooth-blade bucket to final grade just before the working mat is placed. Trim and groom bottom of excavation by hand to the required lines and grades to leave a solid base to receive concrete.
Bearing surfaces for foundation mat shall be compacted with two passes with a vibratory plate compactor or other similar equipment.
Dewatering shall be performed If water has been allowed to accumulate or stand in foundation excavations, such water shall be removed and softened or disturbed soil removed to firm bearing. Excavation and backfilling with Lean Concrete Fill or Compacted Structural Granular Fill of such disturbed or softened soil shall be conducted, at no additional cost to the contract.
Deepening during intermediate stages of excavation shall commence at least 6 meters from the earth support system and then advance in successive stages toward the perimeter of the excavation.
As soon as a section of the required excavation for foundation has been approved by the Engineer, a working mat of the type, thickness and limits proposed by the contractor and approved by the Engineer’s representative, shall be placed over the soil bearing surface within the same work day. If excavation is begun for foundation, which will not be protected by a working mat prior to the end of that workday, the excavation bottom shall remain at least 300mm above the design bottom of foundation bearing level until just before the working mat is placed.
Excavate trenches to the depth indicated or required. Carry the depth of trenches for piping to establish the indicated flow lines and invert elevations.
Grade bottoms of trenches as indicated, notching under pipe bells to provide solid bearing for the entire body of the pipe.
The excavations shall at all times be kept free from storm water, percolating water or subsoil water by any means necessary, on condition not to disturb the excavation surface.
Disposal of excavated materials
A-The following material shall be disposed of legally off the site unless otherwise directed by the Engineer.
1.Unsuitable excavated materials.
2.Excess excavated material.
B-Excess suitable excavated material may, if approved by the Engineer, be deposited in spoil heaps at locations, within the boundary of the Campus, directed by the Engineer.
C-Material resulting from clearing and grubbing operations must not be burnt on the site. Dispose of all such material legally off the Employer’s property and surrounding areas.

Trial Trenches (To check old services )
Safety
Filling and Compacting
Materials:Materials for fill and backfill shall be as hereinbefore specified, obtained from the required excavation on Site, if acceptable, or from borrow sources.
Suitable excavated material for fill and backfill shall be approved by the Engineer. Material, which is suitable for use as fill under exterior slabs and paving and for backfill, shall be separated from material, which is only suitable for general grading.
Provide additional material, if required, at no additional cost to the Employer. Acceptable borrow shall consist of suitable material as hereinbefore specified. Representative samples of each type of borrow material considered suitable shall be delivered to the Engineer for approval.
Place fill materials in horizontal loose layers in such manner as to produce a uniform thickness of material. Placement shall start in the deepest area and progress approximately parallel to the finished grade. Thickness of layers after compacting shall not exceed 200 mm for cohesive soils or 30 mm for cohesion less soils.
1.No fill material shall be placed on areas where free water is standing or on surfaces, which have not been approved by the Engineer.
Compact each layer of fill with equipment to achieve the following percentages of maximum density at optimum moisture content when tested in accordance with ASTM D1557:
LOCATION % MAX. DENSITY
Under Isolated and Continuous Footings. 95
Under Paved Areas and Kerbs. 95
Under Mat Slabs and Slabs on Grade. 95
General Grading. 90
Do not compact soil when the moisture content varies more than 3% from the optimum moisture content. Maintain moisture content by wetting or drying manipulation. Suspend compacting operations when satisfactory results cannot be obtained because of rain or other unsatisfactory conditions.
In lieu of drying by manipulation, hydrated lime, monohydrated lime, or similar beneficial ingredients may be used to reduce the moisture content, reduce the plasticity index, or improve workability. Apply such ingredients in a manner and quantity as recommended by the manufacturer or as required by the Government Testing Station and approved by the Engineer.
Compacting

A.General Compaction:
1. Compact filling after grading and levelling surfaces.
2. Compact filling in layers, adding any necessary extra fill and water, to attain the minimum dry densities as tabulated in the table appended at the end of this Section.
3. Compact filling using vibratory plate, roller or other approved equipment, making the required number of passes with the equipment to obtain specified densities. Each trip of equipment shall overlap the previous trip by 500mm.
4.Confine compaction operations to areas adequate in size for establishing an orderly pattern of compaction.
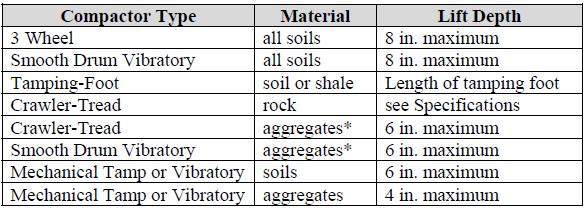
Compacting equipment requirements vary from contract to contract. A list
of the types of compactors which are most commonly used include:
1) Three wheel roller
2) Smooth drum vibrator roller
3) Vibratory tamping roller
4) Static tamping roller or sheepsfoot
5) Crawler-tread equipment or bulldozer
6) Mechanical tamps or vibrators
Testing of Sub grade and Fill Layers:Sub grades and fill layers shall be approved by the Government Testing Station and the Engineer before construction of any further work thereon. Tests of sub grades and fill layers shall be taken as follows:
1.The top 300 mm of sub grade resulting from excavation shall have the maximum density at optimum moisture as hereinbefore specified. In fill areas, each layer of fill shall meet the required density as hereinbefore specified. Make at least one (1) field density test of the sub grade for every two hundred square meters (200 M2) of isolated and continuous footings, paved area, or slabs on grade, but in no case less than three (3) tests. In each compacted fill layer, make one (1) field density test for every overlaying two hundred square meters (200 M2) of isolated and continuous footings, paved area or slabs on grade, but in no case less than three (3) tests. Perform field density tests in accordance with ASTM D1556 or ASTM D2167.
2.At foundation wall backfill take at least three (3) field density tests (ASTM D1556 or ASTM D2167) at locations and elevations as directed by the Engineer.
Destiny test tools
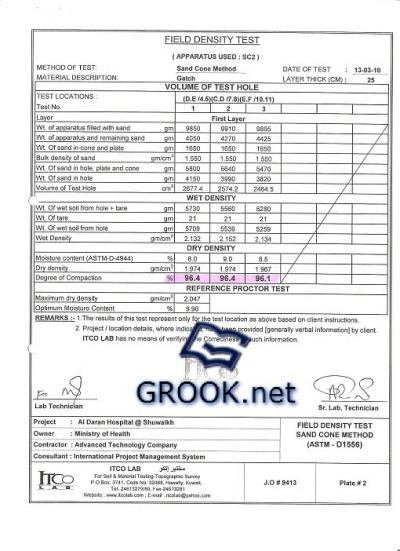
Destiny Test report
Grading
Excavation is followed by grading which involves leveling of the excavated surface. The surface is filled with the excavated soil leaving behind the unsuitable materials. A specific slope is also given such as foundation, surface drainage, base course for road or railway and for landscape and garden improvements.
The filling of holes or ties to form a gravel lot or grade crossing is also known as grading. The soil or material used for filling is known as ‘grade dirt’. Final procedure involves hauling which involves transferring the debris from construction site to the dumping site. Hauling is a much needed process since the debris obtained after demolition, excavation and grading needs to be dumped to proper dumping site in order to avoid obstructions from debris on the construction site.
The process of demolition, excavation, grading and hauling is done by contractors. The contractors providing these services possess heavy equipments required for these processes. The contractors are hired for demolishing, excavating, grading and hauling services for residential, commercial and civil engineering projects. These contractors also provide Bob Cat services which includes use of heavy equipments used for construction. Normally a bulldozer is used for demolishing enormous structures. Heavy equipments like bulldozers, hydraulic attachments such as breaker, grapple or an auger, loaders and compacts are used while excavation works.
The equipments used in these processes need proper training in order to complete the work efficiently and safely. Improper and untrained workforce to maneuver these equipments can result in accidents and can even cost lives.
Final Grading:
Grade the top surface of filling after compaction to give a uniform surface within specified tolerances (+ 3 cm)
Fix Axis and project Corners
Total station Device
Levelling Device
Termite Control
Termites are a group of eusocial insects that, until recently, were classified at the taxonomic rankof order Isoptera (see taxonomy below), but are now accepted as the epifamily Termitoidae, of the cockroach order Blattaria. While termites are commonly known, especially in Australia, as "white ants," they are not closely related to true ants.
This is a treatment that protects the buildings by creating a chemical seal barrier between the soil and the building floor so that no termites will enter the building from below the ground.
The surface area between the ground beams , before concrete is poured it is treated by power spraying the entire area with the anti termite chemicals.
Materials
A. Toxicant Chemical: Water based emulsion, uniform composition, synthetic dye to permit visual identification of treated soil, of the generic chemical chlordane, aldrin or dieldrin.
MIX DILUTION
A. Dilute toxicant chemical aldrin or dieldrin to a 0.5 percent solution.
B. Dilute toxicant chemical chlordane to a one percent solution.
Application
A. Apply toxicant immediately prior to installation of slab-on-grade or finish grading outside foundation walls.
B.Apply toxicant in accordance with manufacturer's instructions.
C. Apply toxicant to soil at the following rates, using metered applicator:
1. Under floor slabs-on-grade: 5 litres/m2.
2. Both sides of foundation wall 6 litres/linear metre/300 mm depth of soil backfilling.
D. Apply extra treatment to structure penetrations, pipe, ducts and other soil penetrations.
E. Apply as a coarse spray to ensure uniform distribution.
F.Coordinate soil treatment at foundation perimeter with finish grading and landscaping work to avoid disturbance of treated soil.
Build a house @ Grook.net